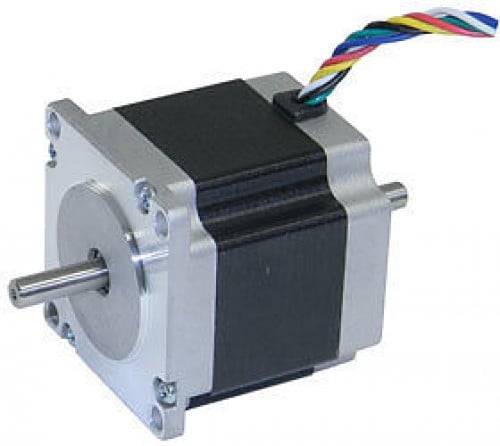
NEMA 17 is a hybrid stepping motor with a 1.8° step angle (200 steps/revolution). Each phase draws 1.2 A at 4 V, allowing for a holding torque of 3.2 kg-cm. NEMA 17 Stepper motor is generally used in Printers, CNC machines and Laser Cutters.
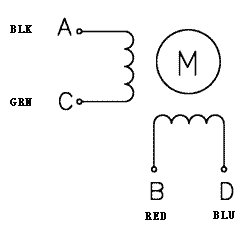
NEMA17 Stepper Motor is commonly used in CNC machines, Hard Drives and Linear Actuators. The motor have 6 lead wires and rated voltage is 12 volt. It can be operated at lower voltage but torque will drop. These motors has a step angle of 1.8 deg., this means that it has 200 steps per revolution for every step it will cover a 1.8° hence the level of control is also high. These motors run on 12V and hence can provide high torque. So if you are looking for a compact easy to use stepper motor with high torque then this motor is the right choice for you.
Operation of Nema17 is similar to normal Stepper Motors. NEMA 17 stepper motor has a 1.7 x 1.7-inch faceplate, and it usually has more torque than the smaller variants, such as NEMA 14. This motor has six lead wires, and the rated voltage is 12 volt. It can be operated at a lower voltage, but torque will drop. Stepper motors do not rotate they step, and NEMA17 motor has a step angle of 1.8 deg. means it covers 1.8 degrees in every step. Wiring diagram for NEMA17 is given below.

Stepper Motor Applications
CNC machines
Precise control machines
3D printer/prototyping machines (e.g. RepRap)
Laser cutters
Pick and place machines
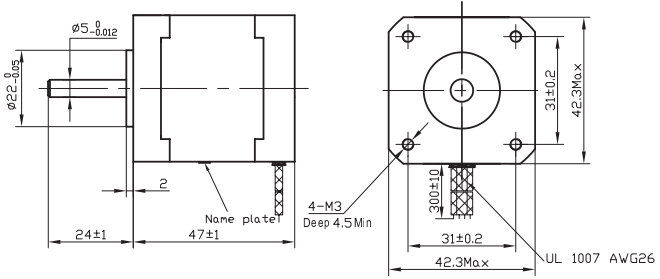
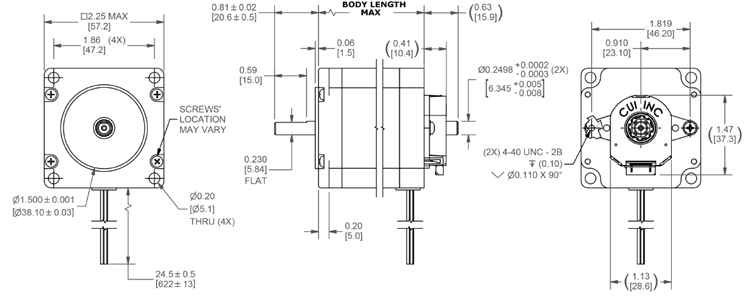
NEMA17 Dimensions